Revolutionising Paramedic Training with High-Fidelity Medical Simulation
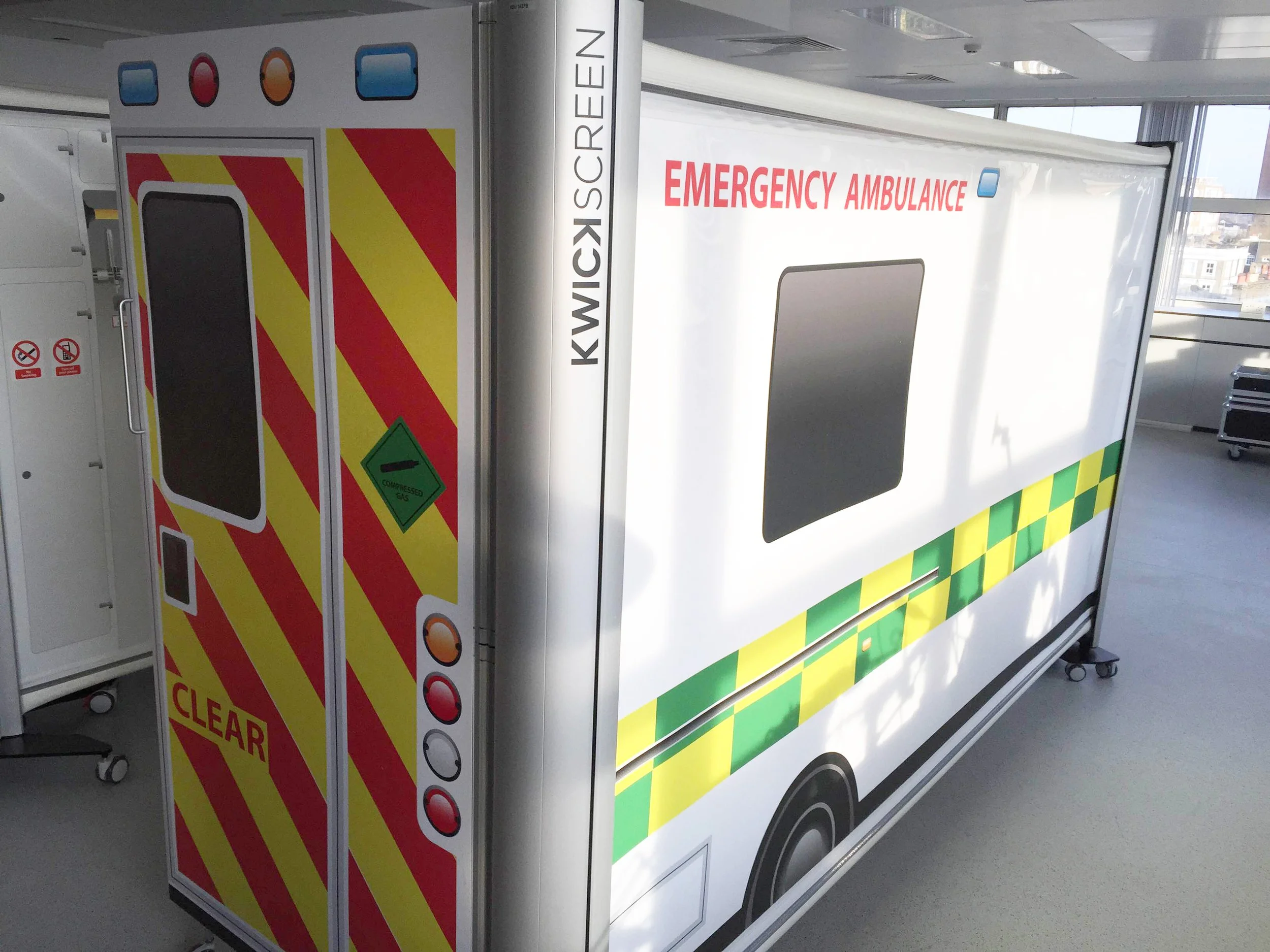
High-fidelity training environments are transforming paramedic training, enabling practitioners to hone their skills safely before facing real-life emergencies. The Centre for Engagement and Simulation Science (ICCESS) at Imperial College London, in collaboration with KwickScreen, created the "Simbulance" – a portable simulation ambulance that is revolutionising medical training.
The Simbulance: A Leap Forward in Medical Simulation
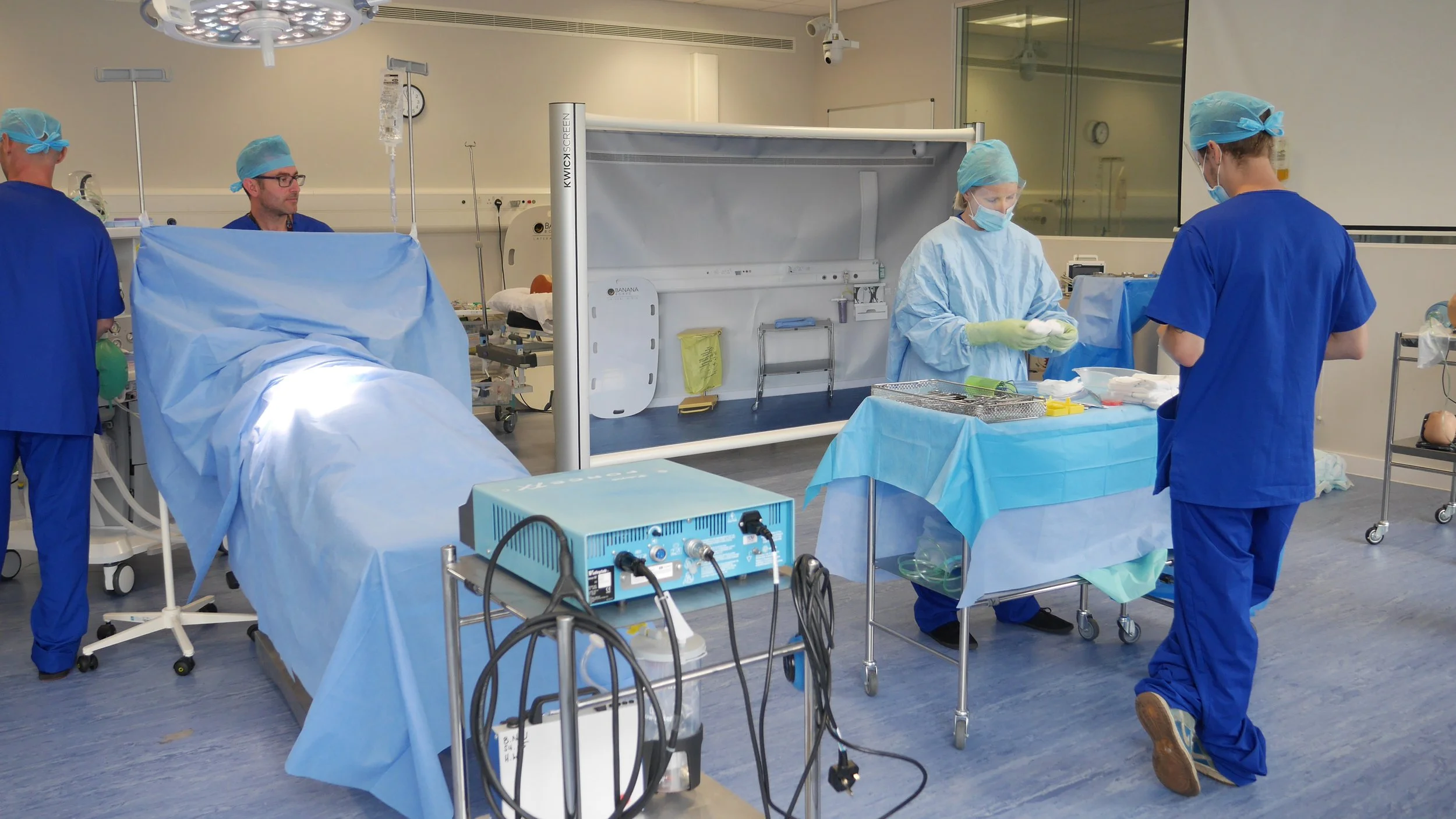
The Simbulance, developed by ICCESS and KwickScreen, replicates the challenges of providing medical care in an ambulance. This portable, foldable simulation environment allows paramedics to practice and refine their skills, ensuring they are well-prepared for real-life patient care.
Key Features and Benefits
Realistic Training Environment: The Simbulance provides a high-fidelity simulation of an actual ambulance, allowing trainees to use their equipment and configure the space as needed.
Portability and Ease of Use: The KwickScreen technology enables quick setup and retraction, making it easy to transport and store, thereby expanding the reach of medical education.
Cost-Effectiveness: The Simbulance offers a cost-effective alternative to traditional training ambulances, with a small storage footprint and ease of deployment.
Enhanced Training Scenarios: Interchangeable panels facilitate various training exercises, ensuring paramedics are prepared for a wide range of situations.
High-Fidelity Simulation: Elevating Paramedic Training: High-fidelity simulation has advanced with sophisticated mannequins replicating realistic patient conditions. The Simbulance further enhances training by providing an environment mimicking the spatial constraints and pressures of a real ambulance.
Sequential and Distributed Simulation
ICCESS uses Sequential Simulation (connected scenarios) and Distributed Simulation (various locations) to enhance training programs, making high-fidelity environments more accessible. Sequential Simulation (SqS) is the physical process of simulating selected aspects of a patient's care pathway. SqS has the potential to simulate an infinite number of scenarios and care pathways. Its application is wide and can be used for a variety of objectives such as a maternity pathway consisting of a GP surgery, maternity clinic and ultrasound clinic. Distributed Simulation, on the other hand, involves low-cost, portable equipment and backdrops that provide 'realistic enough' recreations of clinical settings. This allows medical simulation to be delivered in any type of venue, without the need for costly dedicated facilities.
Integration and Benefits
The integration of Sequential and Distributed Simulation provides a comprehensive and flexible training framework that enhances realism and accessibility. Key benefits include:
Enhanced Realism: The combination of sequential and distributed elements creates highly realistic training environments that closely mimic real-world scenarios.
Increased Accessibility: By distributing simulation resources, ICCESS makes high-fidelity training available to more participants, regardless of their physical location.
Improved Skill Development: Sequential Simulation helps trainees develop skills progressively, while Distributed Simulation facilitates collaborative learning and resource sharing.
A Sequential Simulation utilising Distributed Simulation to portray a patients’ journey from home to hospital via an ambulance.
The Impact of KwickScreen Technology
KwickScreen's retractable screens lend themselves well to both, especially Distributed Simulation. They are flexible, easy to use, and feature high-quality photography to enhance realism. They provide the perfect backdrop for various training environments. The screens retract for neat storage, and zip-out panels allow quick scenario changes. This innovation ensures paramedics are better prepared to meet emergency challenges, enhancing patient care quality.